Hi, I’m Makoto, a freelance engineer.
In this article, I’ll explain Zero Trust and defense in depth.
Although Zero Trust and defense in depth are general security terms, they are topics covered in the AZ-900 exam. I’ll also explain “Conditional Access,” one of the features of Microsoft Entra ID that helps implement Zero Trust. Please read to the end!
Let’s get started!
What is Zero Trust?
Before explaining Zero Trust, let’s review the traditional security model.
Perimeter Security (Traditional Approach)
In the traditional on-premises environment, networks fell into two categories:
- External (Internet)
- Internal (Company network)
They were separated by installing a firewall at the perimeter. This security model is called “perimeter security.
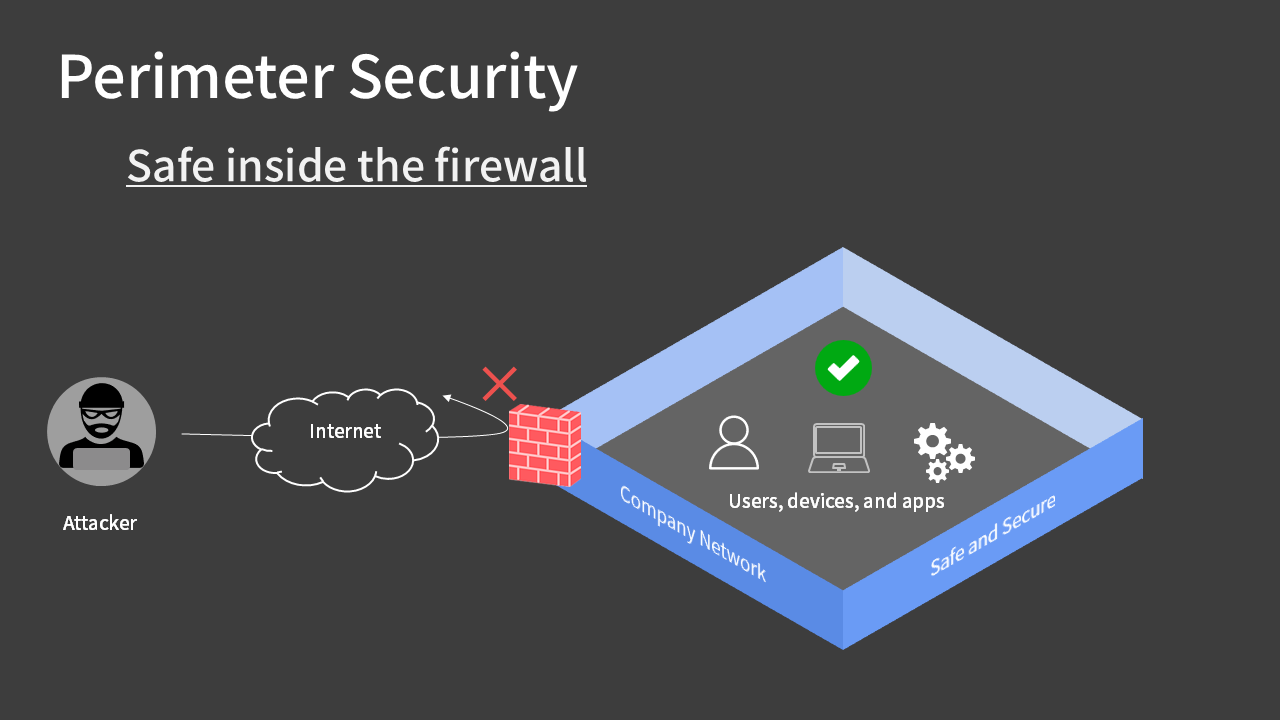
External intrusions have been tightly controlled by the firewall, based on the idea that everything inside the company network (users, devices, applications, data) is safe and trusted.
In recent years, however, the proliferation of public cloud computing has increased the number of ways to connect to data and applications over the Internet, and the boundaries of networks have become blurred.
In addition, the spread of the COVID-19 virus has led to the widespread adoption of remote working, significantly changing the way we work.
Perimeter security is no longer up to the task of enabling flexible work styles that are unrestricted by time, place, or device. As a result, a new security model called “Zero Trust” has gained attention.
Zero Trust (New Approach)
Zero Trust can be summarized as the approach of not trusting anything. The level of trust is 0, hence the name Zero Trust.
In today’s world, where perimeter-based security has become less relevant, this approach suggests that we should be suspicious of everything that accesses our systems and constantly verify that it’s legitimate access. For this reason, the new boundary is said to be “ID”.
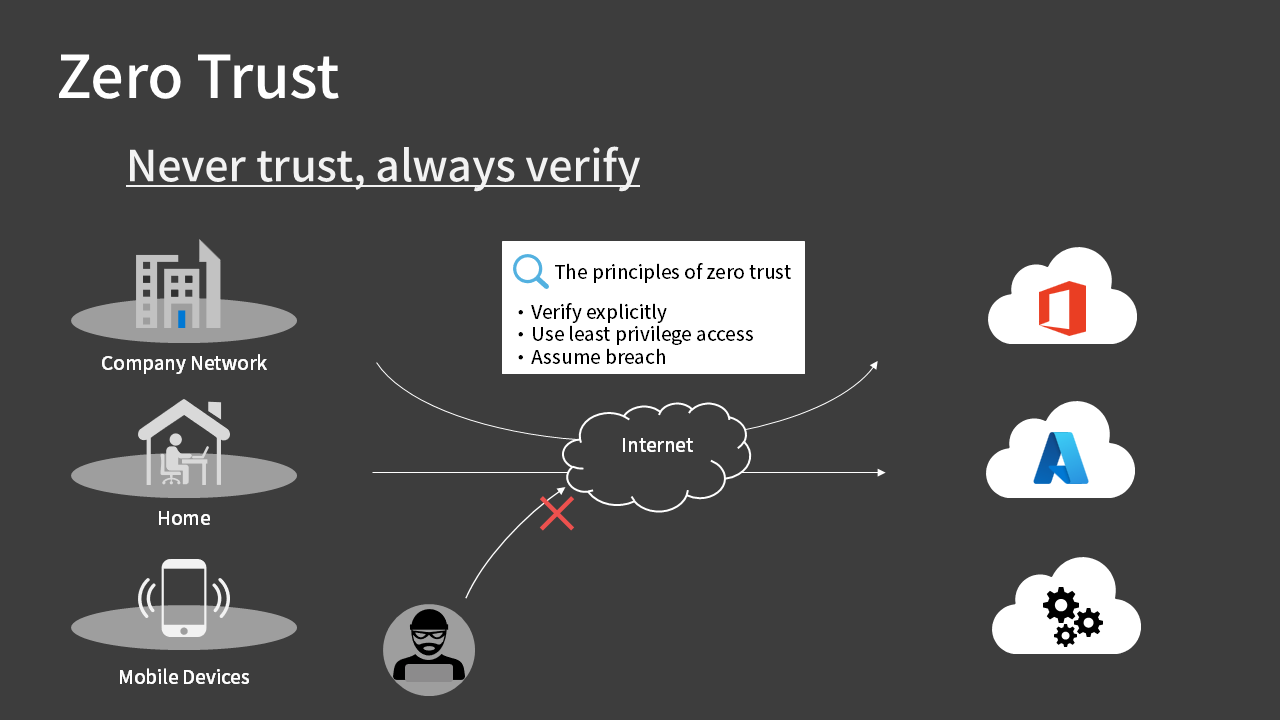
The principles of Zero Trust are:
- Verify explicitly
- Use least privilege access
- Assume breach
The following services are available as solutions for implementing Zero Trust in Azure. Conditional Access, described later, is one of them.
- Microsoft Entra ID for integrated identity management
- Microsoft Intune for device management
- Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management for assigning time-bound access
- Microsoft Sentinel for log aggregation, analysis, and threat detection
Reference:
The term “Zero Trust” has been around for a while. It was first proposed by Forrester Research in the United States in 2010.
What is Defense in Depth?
Another important security concept is defense in depth.
Defense in depth is a strategy that implements security measures at multiple layers to protect against attacks such as unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Azure’s security measures are also based on this concept, providing different solutions for each layer.
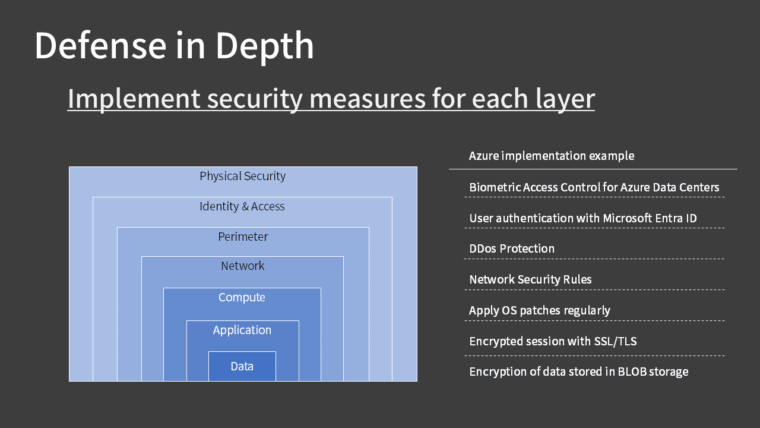
In general, the most important thing to protect is data.
While physical security, such as data centers, is managed by Microsoft, users must consider implementing security measures at every layer, including identity management, network firewalls, and encrypted communications.
What is Conditional Access?
Conditional Access is a mechanism for controlling access to resources based on the state of users and devices. It’s one of the capabilities of Microsoft Entra ID.
It can require MFA for access from certain locations, such as outside the company, or block access from non-compliant devices.
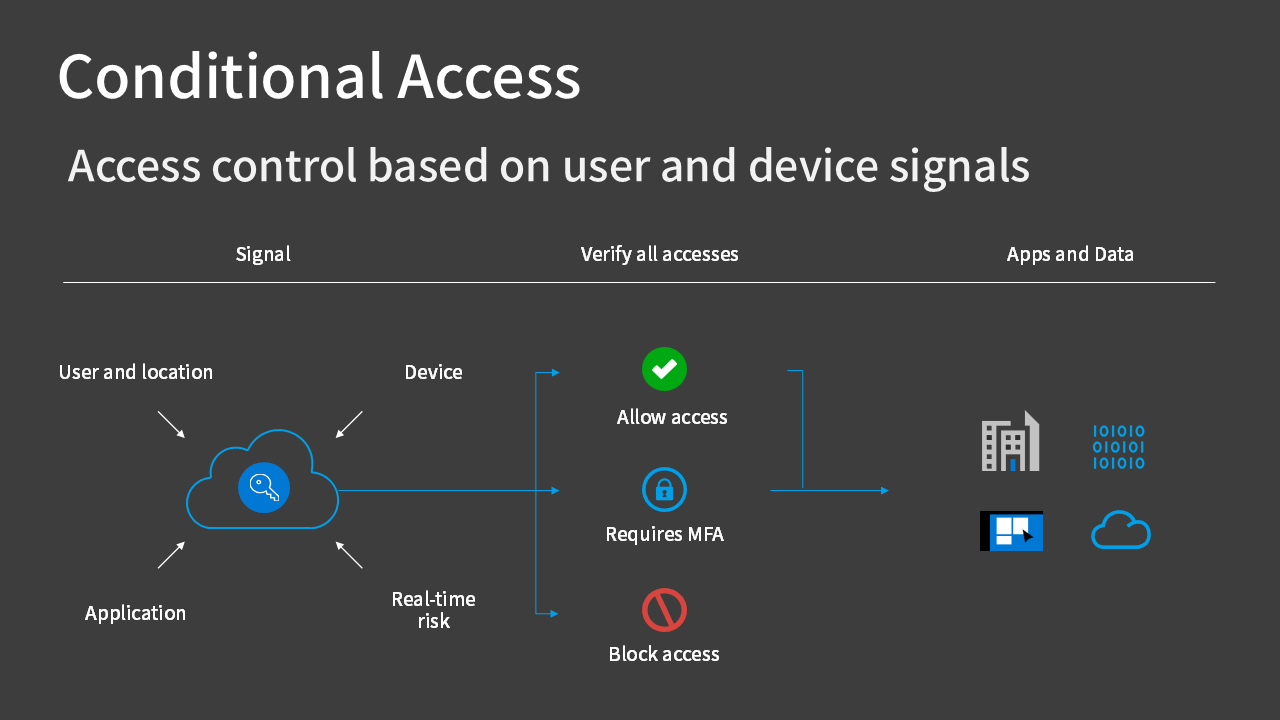
A key feature of Conditional Access is its ability to fine-tune access based on various “signals” such as user, location, and device.
Even for legitimate users, access can be blocked if the location is out of the ordinary (untrusted location) or if the device is not approved (untrusted device).
Conditional access evaluation occurs after authentication (identity verification) is completed by Microsoft Entra ID.
Reference:
To use Conditional Access, you must have a Microsoft Entra ID Premium P1 license or higher.
Summary
In this article, we explained Zero Trust and defense in depth. We also presented an overview of Conditional Access as one of the features for achieving Zero Trust.
Modern security measures require that measures are taken at each layer of the system and that users (IDs) accessing those layers are constantly checked without trust. Let’s make sure we understand the concepts behind these terms.
That’s all for now. See you next time!













